The Application and Development of Precision Injection Molding in the electronics field
Introduction
In the new era, the rapid development of electronic technology drives electronic products toward miniaturization, high performance and multi-functionality. As an advanced plastic molding technology, precision injection molding, with its characteristics of high precision, stability and efficiency, plays an increasingly critical role in the electronics field, becoming an important force supporting innovation and upgrading of electronic products.
I. Demand Characteristics of Precision Injection Molding in Electronics
(1) High Precision Requirements
With the increasing integration of electronic products, internal components become smaller and more complex. For example, micro-connectors and chip packaging brackets in mobile phones require dimensional tolerances controlled within ±0.01mm or even smaller to ensure precise matching between components for efficient signal transmission and stable electrical connections.
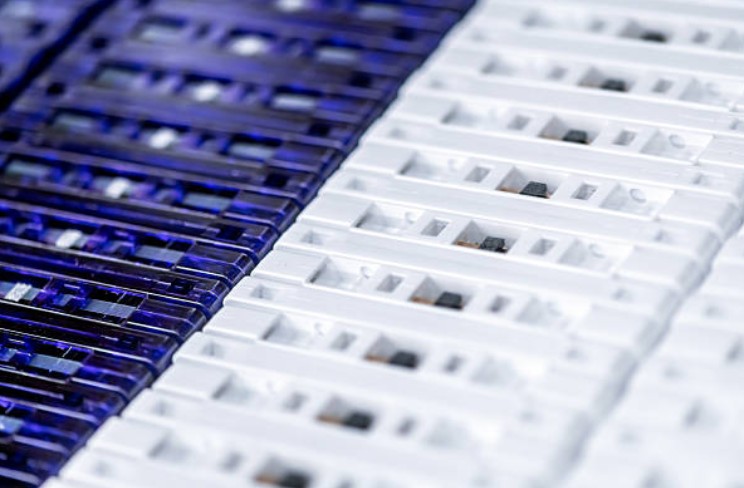

(2) Excellent Surface Quality
The appearance of electronic products directly affects consumers' purchasing decisions. Precision injection molded casings and buttons need superior surface finish, generally with surface roughness below Ra0.1μm, free from flow marks, air streaks or deformation, to present an attractive and exquisite appearance.
(3) Diversified Material Properties
Electronic devices operate in diverse environments, requiring injection materials with different properties. High-temperature components use heat-resistant plastics like PEEK, which works stably at 260°C for long periods. Components needing electromagnetic shielding use plastics with metal powders or special molecular structures to ensure normal operation and reduce interference.
II. Typical Applications in Electronics
(1) Electronic Product Casings
Taking smartphones as an example, precision injection molded casings achieve thin-wall designs (0.5-1mm thickness) while maintaining sufficient strength. High-gloss injection technology creates mirror-like surfaces, enhancing product texture. Similar applications exist in tablets and laptops for appearance and protection.
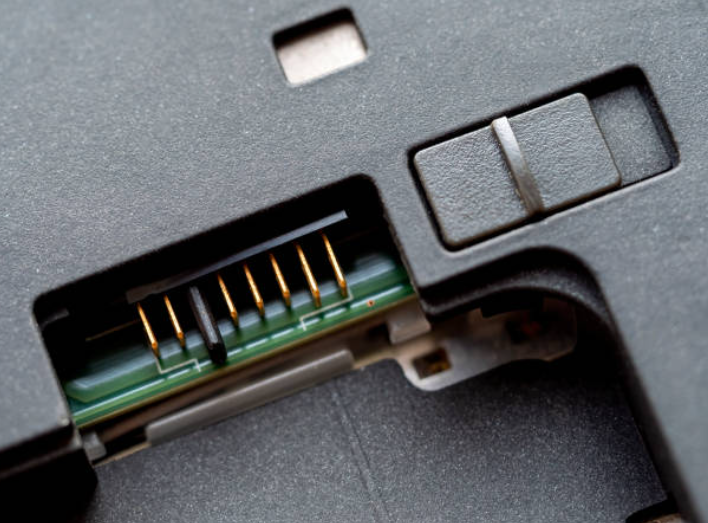

(2) Connector Molding
In 5G communication devices, high-frequency connectors demand extreme precision. Ultra-precision mold technology controls key dimensions within ±0.005mm. Proper insulation materials and precise molding ensure low signal attenuation and strong anti-interference capability, meeting high-speed, large-capacity transmission needs.
(3) Chip Packaging Applications
Precision injection molding manufactures chip packaging housings and lead frames. Epoxy molding compounds form reliable protective layers through precision processes. Precise control of lead frame injection ensures uniform spacing and accurate dimensions, guaranteeing stable connections between chips and external circuits.
III. Key Technological Points
(1) Mold Design and Manufacturing
Molds are core to precision injection molding. CAE software simulates melt flow to optimize gate design. Ultra-precision machining like wire cutting and EDM achieves surface roughness below Ra0.02μm and dimensional accuracy within ±0.005mm.

(2) Injection Process Control
Precise control of temperature (±2°C deviation), pressure and speed is crucial. Parameters are adjusted based on product structure—high speed/pressure for thin walls and low speed/pressure for thick sections. Proper holding pressure and time compensate for cooling shrinkage.
(3) Material Handling and Quality Inspection
Hygroscopic materials like PA undergo drying at 120-150°C for 4-6 hours to reduce moisture below 0.02%. High-precision coordinate measuring machines perform 100% dimensional inspection, while machine vision systems check surface quality.
IV. Development Trends in the New Era
(1) Intelligent Production
With Industry 4.0 and IoT, injection machines equip intelligent control systems. Sensors collect real-time parameters, optimized by big data and AI algorithms. Remote monitoring allows operators to track equipment status via mobile or computer terminals.
(2) Micro-nano Injection Technology
To meet further miniaturization needs, micro-nano injection technology enables manufacturing of micro-components like microfluidic chips with nanoscale precision through new mold materials and specialized processes.
(3) Green Injection Molding
Environmentally friendly injection molding gains attention. Degradable plastics like PLA are developed. Hot runner technology reduces waste, and improved cooling systems shorten cycles, lowering energy consumption to achieve sustainable development.
